What is Coronary Angioplasty, and How Can it Save Your Life?
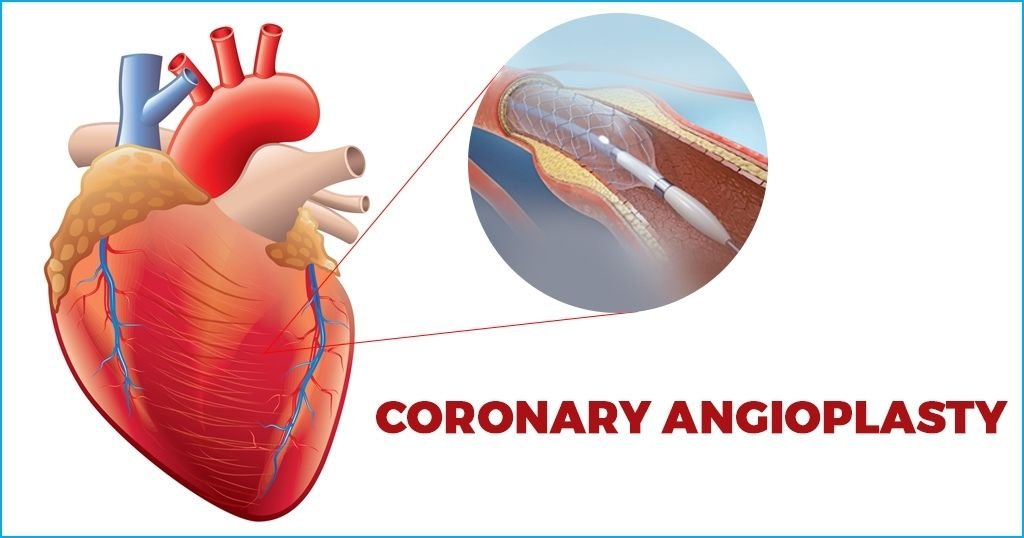
Coronary angioplasty is a life-saving procedure that can quickly restore blood flow to your heart, reducing the risk of a heart attack and relieving chest pain. Think of your heart’s arteries as vital highways, delivering oxygen-rich blood to keep your heart beating strong. Over time, these highways can get clogged with fatty deposits, narrowing the passage and restricting blood flow. This buildup can lead to chest pain, fatigue, and even a life-threatening heart attack. That’s where angioplasty comes in. During this procedure, a tiny balloon is guided through the blocked artery and gently inflated, widening the artery and pushing the blockage aside.
In many cases, a stent is placed to keep the artery open for the long term. With its ability to rapidly improve blood flow and heart function, angioplasty not only relieves symptoms but also reduces future risks.
This blog will explain how coronary angioplasty works and how it can truly save your life.
What Does the Coronary Angioplasty Procedure Involve?
The coronary angioplasty procedure is minimally invasive and is performed by inserting a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm. The catheter is then guided through the arteries to the blocked or narrowed coronary artery. Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated. This balloon pushes the plaque (a fatty deposit of cholesterol) against the artery wall, widening the artery and restoring blood flow to the heart muscle.
A crucial aspect of this procedure is that it doesn’t require open-heart surgery, making it a less risky option for many patients with heart disease. While the balloon widens the artery, it’s often followed by stenting to prevent re-narrowing over time.
When is Angioplasty Recommended?
Angioplasty is typically recommended in cases of coronary artery disease (CAD), where plaque buildup narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow. Over time, this can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack. Doctors often recommend angioplasty when medications or lifestyle changes are not enough to improve blood flow.
Here are some specific scenarios when angioplasty may be recommended:
- Acute heart attack (myocardial infarction): During a heart attack, angioplasty can be an emergency procedure to restore blood flow and minimize damage to the heart quickly.
- Stable angina: If you experience frequent chest pain and your heart’s blood supply is restricted due to plaque buildup, angioplasty may be suggested to ease symptoms.
- Ischemic heart disease: When parts of the heart muscle don’t get enough blood due to narrowed arteries, angioplasty can help restore proper circulation.
In some instances, if the blockages are too severe or if multiple arteries are affected, doctors may recommend bypass surgery instead.
Dr. Dinesh Kumar Mittal, a renowned Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgeon with 20+ years of experience, emphasizes, “Coronary angioplasty is not just a procedure; it’s a step towards reclaiming a healthier life. The key to its success lies not only in the procedure itself but also in the dedicated aftercare and lifestyle changes that follow.”
What is the Difference Between Angioplasty and Stenting?
While coronary angioplasty involves using a balloon to widen a narrowed artery, stenting is often an additional step during the procedure. A stent is a small wire mesh tube that’s inserted into the artery to keep it open after the balloon has done its job. The stent acts as a structure to support the artery walls, reducing the risk of them becoming narrow again.
There are two main types of stents used in angioplasty:
- Bare-metal stents (BMS): These are simple metal tubes that keep the artery open.
- Drug-eluting stents (DES): These stents are coated with medication that helps prevent scar tissue from forming in the artery, further reducing the risk of re-narrowing.
How Much Does Coronary Angioplasty Cost in India?
The cost of coronary angioplasty in India varies widely based on factors such as the hospital, the type of stent used, and whether the procedure is elective or emergency. On average, the expense ranges from INR 1,50,000 to INR 4,50,000 (USD 2,000 to USD 6,000). This estimate typically includes hospital and surgeon’s fees, anaesthesia, and post-procedure care.
Costs can be lower in smaller cities or government hospitals and higher in major cities or private facilities. Patients should consult their healthcare provider and hospital for a detailed cost estimate and to check if insurance coverage is available.
What is Involved in Coronary Angioplasty Aftercare?
After undergoing coronary angioplasty, proper aftercare is essential to ensure the success of the procedure and promote long-term heart health. Recovery from angioplasty usually takes a few days to a week, but long-term lifestyle changes are crucial. Here are some important aspects of aftercare:
- Hospital stay and monitoring: After the procedure, most patients stay in the hospital for 1-2 days for observation. Their heart function is closely monitored to ensure there are no complications.
- Medications: You will likely be prescribed medications to prevent blood clots, reduce cholesterol, and control blood pressure. If you receive a stent, you’ll need to take blood-thinning medications like aspirin or clopidogrel for several months to prevent the formation of clots in the stent.
- Lifestyle changes: A healthy lifestyle is key to preventing further heart problems. This includes a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins; regular physical activity like walking or swimming; and quitting smoking to reduce heart disease risk.
- Follow-up appointments: Your doctor will schedule follow-up visits to assess your recovery and ensure your heart is functioning well. These visits are important for monitoring your condition and adjusting medications if necessary.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: Many patients are advised to join a cardiac rehabilitation program, which is a medically supervised program designed to improve cardiovascular health after procedures like angioplasty. The program includes exercise training, education on heart-healthy living, and counselling to reduce stress.
One of Dr. Dinesh Mittal’s patients shares their experience, saying, “After my coronary angioplasty, the comprehensive aftercare was crucial for my recovery. I stayed in the hospital for a couple of days for monitoring, and I was prescribed medications to keep my heart healthy. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, staying active, and quitting smoking made a big difference.”
Conclusion
Coronary angioplasty is a life-saving procedure that can dramatically improve the quality of life for people with coronary artery disease. By opening up blocked arteries, the procedure restores blood flow to the heart, reducing symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath and preventing more severe conditions like heart attacks. With proper aftercare medications and lifestyle changes, patients can experience significant improvements in their heart health and overall well-being.
Understanding the coronary angioplasty procedure when it’s recommended, how it differs from stenting, and the associated costs can help individuals make informed decisions about their heart health. Always consult with a cardiologist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition and to ensure the most effective care.
FAQs
1. How Long Does the Coronary Angioplasty Procedure Take?
The procedure typically takes 30 minutes to 2 hours.
2. What Are the Risks Associated with Coronary Angioplasty?
Risks include bleeding, artery re-narrowing, blood clots, or rare heart attack or stroke.
3. Can Coronary Angioplasty Be Performed on All Blocked Arteries?
Not all blockages are suitable; some may require bypass surgery.
4. How Soon Can I Resume Normal Activities After Angioplasty?
Light activities can usually be resumed within a week, but heavy exertion takes longer.
5. Can Angioplasty Prevent Future Heart Attacks?
It reduces the risk, but prevention also depends on lifestyle changes and medications.
Explore more blogs: What Post-Operative Care is Needed After Open Heart Surgery?
